Propelled by Igor Stravinsky’s score, continuous energy courses through “Symphony in Three Movements” as the dancers, explained Balanchine, “try to catch the music and do not, I hope, lean on it, using it instead for support and time frame.”[note]Notes for “Symphony in Three Movements,” The George Balanchine Trust, http://balanchine.com/symphony-in-three-movements/[/note]
Energy flexes its feet, and with outstretched arms, it flexes its hands too. Sometimes with palms visible and other times with fingers tipped upward as if emulating an aeroplane. Off-centred or with legs turned inward, it proudly alters the lines of the classical body. In choreography that is as transparent with its complexity-of-step and precision-required as it is bold, the feeling conveyed to me was one of an endless force. Though the curtain to my view came down and the dancers changed, somewhere, in some alternate world, it continued, unimpeded and unfading, a conversation between Balanchine and Stravinsky, between harp and piano, a great sweaty, unfailing machine. If you listen closely, you can hear the swish of a dancer’s long ponytail as it comes unstuck from her dampened brow. [note]“Ty King-Wall on ‘Symphony in Three Movements,’” Behind Ballet, September 3 2015 http://www.behindballet.com/ty-king-wall-on-symphony-in-three-movements/[/note]
It is little wonder that performing within such a whirlpool of physicality, as Ty King-Wall explained, “is hard, and confusing! I’ve never been much of a ‘counter’ when I dance, I prefer to listen to the melody and take my cues from the highlights I hear in that. For this ballet, that’s impossible: we do a lot of dancing together, or in canon, so you need to be really precise! For example, there is a section in the third movement, the Fugue, where the three principal men dance together. We count it in tens, but the first four counts of the first two tens are in silence! All three of us then do the same piece of choreography, but in a two-count canon, and all facing a different direction!”
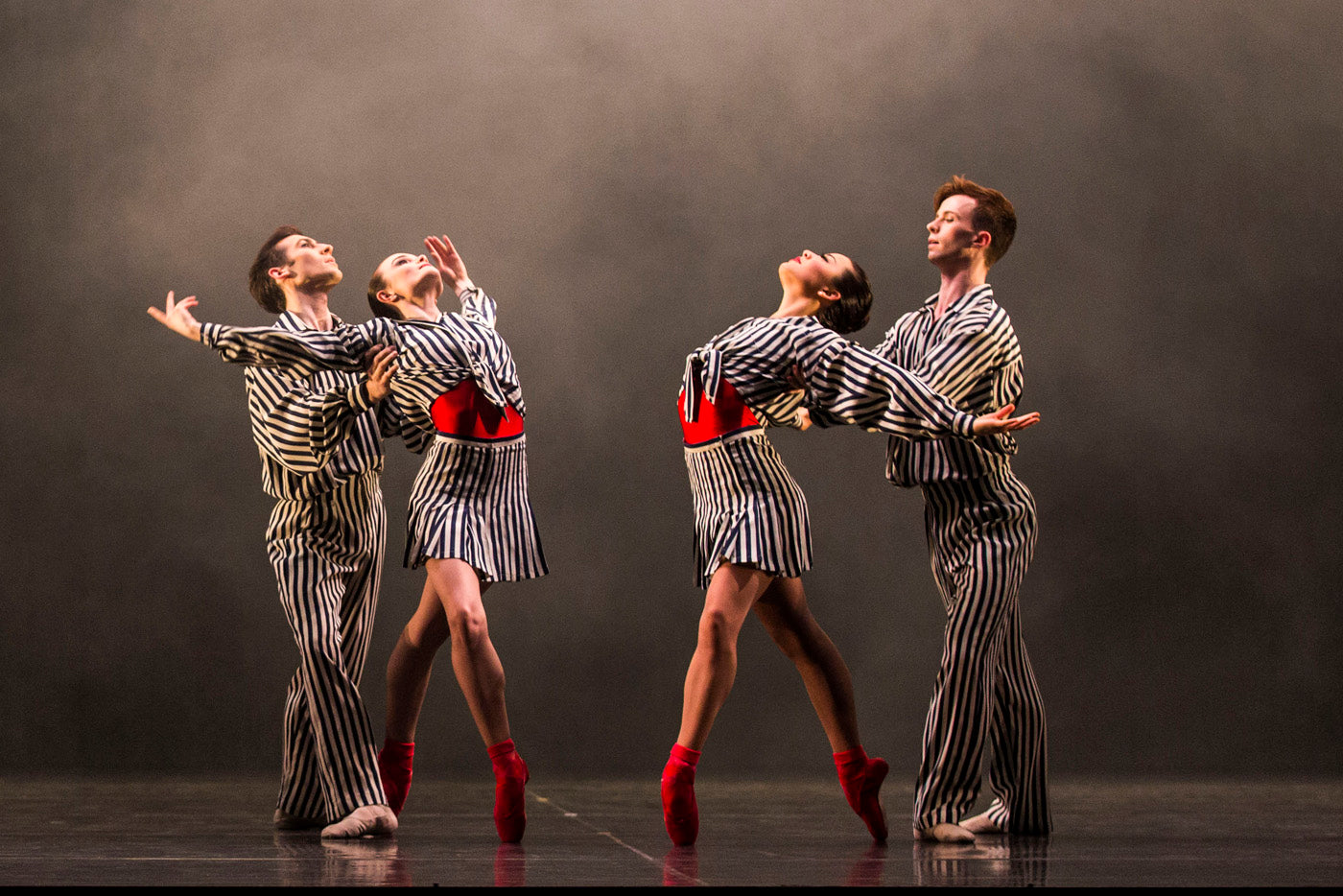
Stravinsky’s score, which premiered in 1946, is as indivisible from Balanchine’s choreography, which premiered in 1972 in honour of the composer, as “the myriad influences that …. suffuse ‘Symphony in Three Movements.’” There are references to the 1940s musical movies of Busby Berkeley and Esther Williams, embodied by Balanchine’s opening patterns of sexy, leggy, pony-tailed women; to the jazz era, which Balanchine evokes through syncopation and brisk athletic steps; to jitterbug and swing; and to the Asian culture that so captivated Stravinsky in the 1940s …. There is a combative element and relentless drive….”[note]Jane Albert, “The Big Bang,” The Australian Ballet 20:21 programme, Arts Centre, Melbourne, Australia, 9[/note] And yet within this controlled intensity there is also calmness, as exemplified by the graceful and angular-shaped pas de deux performed by Rudy Hawkes and Amber Scott in the second movement.[note]Where the first movement was intended for a documentary on China, and the third movement was created in response to newsreel footage of German soldiers, the lyrical second movement was originally composed for Franz Werfel’s The Song of Bernadette, though a full film score was never completed.[/note]
Playfully, tenderly, hands touched, but didn’t, and one body enfolded around another like a sigh. With assured, slow strokes, they momentarily appeared to swim across a lake, each in complete awareness of the other, and of each part of their own bodies, connected by movements that saw one yield as the other surfaced, and by what appeared as a shared space of concentration.
From the twentieth century, the program sparked to the present day with Harbour’s “Filigree and Shadow” in raw sound electronic conversation with Siegfried Rössert and Ulrich Müller of 48nord. The orchestra having gone home, their pit now darkened, the movement set in motion by “Symphony in Three Movements” was supercharged, accelerated.
The movement, in this ballet, is weighted and earthbound, and primal in its directness. Rooted to and of the present, the movement is in a language I can easily read. It is familiar, this shadowed tension, but not expected. Above all, there is freedom of movement, of expression, of difference. Though the twelve dancers—eight male, four female—were all dressed alike and at times loomed like a pack of hunters as they carved through the space, to me, they were primarily individual, real, known. Jill Ogai had shed the satin greasepaint and costumed fleshiness of “Cinderella’s” Dumpy Stepsister—though perhaps her confident swagger laid bare something altogether more sinister. Perhaps behind the curved wall within an angled cell, designed by Kelvin Ho, there lay a disposed-of Dumpy. Silhouette altered: hair that was formally up high in a Balanchine ponytail was now worn in a loose bob that at times shielded the face or scraped back in a low ponytail, or a small man-bun, as befitted the sounds of “astringent horns recur[ing] like distant alarms, strings vibrat[ing] with laboratory precision, and underneath it all …. a propulsive industrial hum: a machine that’s never turned off.”[note]Kate Scott, “Permanent Acceleration,” The Australian Ballet 20:21 programme, 23[/note]
Charged with “being aggressively present,”[note]Tim Harbour’s Filigree and Shadow: First Glimpse, The Australian Ballet's YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bpkl10emWb8 [/note] forged from the landscape and appearing to glory in it, Tuesday’s stalking cast: Andrew Killian, Rudy Hawkes, Calvin Hannaford, Luke Marchant, Cameron Hunter, Shaun Andrews, Charles Thompson, Christopher Rodgers-Wilson, Dimity Azoury, Vivienne Wong, Alice Topp, and Ogai. Wong and Killian, together, like metal conducting heat—are their cores aluminium, iron, or silver? Azoury, with blackened eyes, direct and powerful, from a plough-like pose, raised one leg skyward, and, with Hawkes’ aid, all but pulled herself upright to a standing-split. In choreography so furious-and assured-of-pace—I did see that, didn’t I? “A lot of the movement sits in the upper body, and the articulation you can get just from using your wrists, fingers, elbows and shoulders.”[note]Tim Harbour quoted by Rose Mulready, “The Heart of the Storm,” The Australian Ballet 20:21 programme, 13[/note] Whether hawking above the shallows or with shoulders and backs rounded to simulate a cartoon villain walking high up on their toes, throughout the performance I’d no idea what was next nor where to look as the intensity built. This sensation reminded me of Marlon Brando’s own acted-upon advice to never pause for too long in an open doorway, all but telling the audience you’d not done speaking. Instead, Brando favoured keeping an audience ‘on their toes,’ and this too, seems Harbour’s intent.
In part prompted by the innate survival techniques employed by birds in cyclone, “Filigree and Shadow” draws more on a sense of inner strength than one of menace. The dancers echoed birds fired like a slingshot from a storm’s nucleus. Buffeted by high winds, they correct their course, or with passerine ‘locked down’ wings they ‘rode out’ the elements. With every muscle (or wing) wrung out like a wet towel, to me, this highly emotional work feels like it is about how we respond to a challenge. Instability and migratory marathons are best faced with fervency. I am rendered envious of the dancers’ cathartic liberation and this perhaps would almost be cruel—such expression, free-prowling whilst I sit immobile in the theatre, caught literally in Benjamin Cisterne’s industrial headlights—where it not for the buoyancy and inclusiveness of Tharp’s “In the Upper Room,” which feels on the threshold of a dream-state and waking.
Through the haze, my eyes tried to bring the forms in focus as they advanced and receded. Where it began and where it ended, I could not tell, and the effect: magical. Having held my breath earlier in Harbour’s shadows, I was again caught off guard, swept up by the playful, hypnotic nonchalance of the ‘stompers’ in their runners and ‘bomb squad’ in their red pointe shoes. Once more, Azoury and Wong (as ‘stompers’ on the Wednesday night performance) completely inhabited their roles with such joyful drive. And in the darkened void, Natasha Kusch, Ako Kondo, and Miwako Kubota (as the ‘bomb squad’), as one friend described, materialised as Paul Klee’s Dance of the Red Skirts (1924). Nicola Curry’s open embrace saw her meet every head-waggle from left to right in a demanding work (to perform) that brings together quick reflections of boxing, tap, and yoga.[note]Nicola Curry, “My life as a stomper,” Behind Ballet, August 26, 2015, http://www.behindballet.com/my-life-as-a-stomper/[/note]
Brett Simon, Callum Linnane, and Richard House dug into the stage’s foundations, but really to single out the few belies the brilliant strength of all six casts I saw perform on both nights I attended.
Layered, repeated and varied movement, chased by Philip Glass’ persistently melodic Dances I through IX, “In the Upper Room” typifies Tharp’s belief that dance allows for thoughts (and emotion) in movement. With a score that “hints at things, but …. Leave[s] a lot of space for the dance to happen… [allowing] the dancers [to] complete it, fill it in,”[note]Philip Glass, quoted in the synopsis of Twyla Tharp’s “In the Upper Room,” http://www.twylatharp.org/content/upper-room[/note] I defy anyone to wish that this performance would end. But then it doesn’t, does it, for I’ve discovered the source of perpetual motion and its euphoric energy is down right infectious.
*cue choral singers (Dance IX)*



comments